Sass 基础
Saas 环境搭建与基本语法
- 下载 Visual Studio Code
demo.scss
.header{
span{
color: red;
&:active{
color: green;
}
&:hover{
color: blue;
}
}
}demo.sass
.header
span
color: red;
&:active
color: green
&:hover
color: blue- css
.header span {
color: red;
}
.header span:active {
color: green;
}
.header span:hover {
color: blue;
}变量入门
$small-font:14px+3px;
$text-color:#555;
$default-font:'microsoft yahei';
.title{
color: lighten($text-color,20%);
font-size:$small-font;
font-family: $default-font;
}
.subtitle{
color: darken($text-color,20%);
font-size:$small-font;
}.title {
color: #888888;
font-size: 17px;
font-family: "microsoft yahei";
}
.subtitle {
color: #222222;
font-size: 17px;
}
/*# sourceMappingURL=demo.css.map */嵌套,代码拆分及引入
- 嵌套
div{
span{
color: red;
a{
color: blue;
}
}
}
css
div span {
color: red;
}
div span a {
color: blue;
}- 代码拆分
_vir.scss [私有的 scss 文件,用于其他的引用] 不会生成 vir.css
main.scss
@import 'vir';
@import 'header';
@import 'content';
_vir.scss
$color:red;
$content-color:orange;
_header.scss
.header{
color: $color;
background-color: $content-color;
}Mixin 混入的使用
- 公共部分的拆分
- _mixins.scss
@mixin singleline-ellipsis($width) {
width: $width;
overflow: hidden;
white-space:nowrap;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}
- main.scss
@import 'mixin';
.text{
@include singleline-ellipsis(600px);
}
.content-text{
@include singleline-ellipsis(1000px);
}媒体查询与 Mixin 的配合使用
- main.scss
@mixin ipad($height) {
@media screen and (min-width:768px) {
height:$height;
@content;
}
}
.header{
width: 1000px;
@include ipad(100px){
width: 500px;
}
}
- main.css
.header {
width: 1000px;
}
@media screen and (min-width: 768px) {
.header {
height: 100px;
width: 500px;
}
}Vue 语法初探
初学编写 HelloWorld 和 Counter
//fixed 固定在底部
<div class="footer">
MIT Licensed | Copyright © 2022-present Damogu
</div>
.footer{
position fixed
height 2rem
bottom 1.2rem
left 50%
width 100%
}
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Hello World</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
data(){
return {
content:1
}
},
mounted(){
setInterval(()=>{
this.content+=1;
},1000)
},
template:'<div>{{content}}</div>'
}).mount('#root');
</script>
</html>编写字符串反转和内容隐藏小功能
- 反转
Vue.createApp({
data(){
return {
content:'hello world'
}
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick(){
//vue 里面不会面向 dom 编程,是面向数据编程 this.content=this.content.split('').reverse().join('');
}
},
template:
`
<div>
{{content}}
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">反转</button>
</div>
`
}).mount('#root');- 显示隐藏内容
Vue.createApp({
data(){
return {
show:true,}
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick(){
this.show=!this.show;
}
},
template:
`
<div>
<span v-if="show">hello world</span>
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">显示/隐藏</button>
</div>
`
}).mount('#root');编写 TodoList 小功能,了解循环和双向绑定
Vue.createApp({
data(){
return {
inputValue:'',
list:[]
}
},
methods:{
handleAddItem(){
// console.log(this.inputValue);
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue='';
}
},
//1.在某个属性上需要绑定内容:v-bind:title="inputValue"
//2.增加 {{inputValue}},在标签内部
template:`
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue" />
<button
v-on:click="handleAddItem"
v-bind:title="inputValue"
>
增加
</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) of list">{{item}} {{index}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
`
}).mount('#root');组件概念初探,对 TodoList 进行组件代码拆分
const app= Vue.createApp({
data(){
return {
inputValue:'',
list:[]
}
},
methods:{
handleAddItem(){
// console.log(this.inputValue);
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue='';
}
},
//1.在某个属性上需要绑定内容:v-bind:title="inputValue"
//2.增加 {{inputValue}},在标签内部
template:`
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue" />
<button
v-on:click="handleAddItem"
v-bind:title="inputValue"
>
增加
</button>
<ul>
<todo-item v-for="(item,index) of list"
v-bind:content="item"
v-bind:index="index"
/>
</ul>
</div>
`
});
app.component('todo-item',{
props:['content','index'],
template:'<li>{{index}}--{{content}}</li>'
});
app.mount('#root');Vue 基础语法
Vue 中应用和组件的基础概念
//createApp,创建一个 vue 应用,存储到 app 变量中
//传入的参数表示,这个应用最外层的组件,应该如何展示
//mvvm 设计模式, m->model 数据, v->view 视图, vm->viewModel 视图数据连接层
const app= Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
message:'hello world'
}
},
template:"<div>{{message}}</div>"
});
//这应用只作用于 id 等于 root 的 div 元素上去
//vm 代表的就是 vue 应用的根组件
const vm= app.mount('#root');
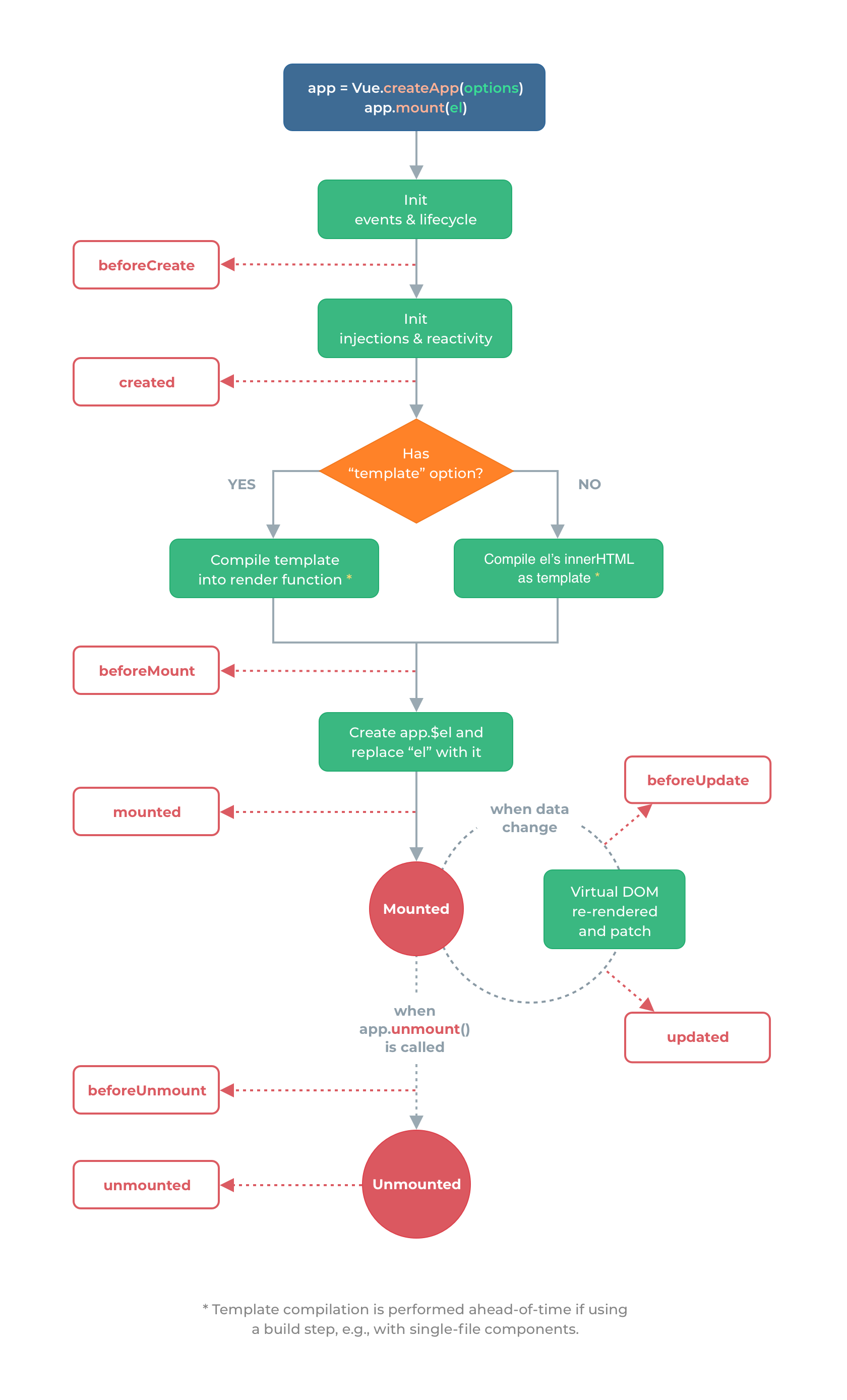
//在 F12 中输入 vm.$data.message[操作数据,改数据]理解 Vue 中的生命周期函数
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 如果没有最下方的 template,则↓ -->
<div>{{message}}</div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
//生命周期函数:在某一时刻会自动执行的函数
const app= Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
message:'hello world'
}
},
//在实例生成之前会自动执行的函数
beforeCreate(){
console.log('beforeCreate');
},
//html 渲染的瞬间
//在实例生成之后会自动执行的函数
created(){
console.log('created');
},
//在组件内容被渲染到页面之前自动执行的函数,[挂载之前执行的函数]
beforeMount(){
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'beforeMount');
},
//在组件内容被渲染到页面之后自动执行的函数,[挂载之后执行的函数]
mounted(){
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'mounted');
},
//当数据发生变化时会立即自动执行的函数 vm.$data.message='bye' 改变数据时
beforeUpdate(){
//<div>hello world</div> beforeUpdate
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'beforeUpdate');
},
//当数据发生变化,页面重新渲染后,会自动执行的函数
updated(){
//<div>bye</div> updated
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'updated');
},
//app.unmount()
//<div>hello world</div> beforeUnmount
//unmounted
//当 Vue 应用失效时,自动执行的函数
beforeUnmount(){
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'beforeUnmount');
},
//当 Vue 应用失效时,且 dom 完全销毁之后,自动执行的函数
unmounted(){
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'unmounted');
},
// template:"<div>{{message}}</div>"
});
const vm= app.mount('#root');常用模版语法讲解
const app= Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
message:"hello world",
show:false,
name:'title1',
event:'mouseenter'//动态参数
}
//2. return{
// disable:false //可输入
// }
},
//6. v-on:click="handleClick"
methods:{
// 一定要写在 methods 上
handleClick(){
alert('click')
}
},
//1. v-html="message" 加粗 <strong>hello world</strong>
//如果你的属性值想去显示数据变量内容的话,要用 v-bind:title="message"
//2. 控制是否输入内容的状态
// template:`<input v-bind:disable="disable"/>`
//3. {{ JS 表达式 }}
//4. v-once:第一次展现 hello world,后面一直就展现 hello world,不会管 message 变化
//降低一些无用的渲染,提高渲染的性能
//5. v-if="show" 显示,隐藏<div ←>
//7. v-on: 简写 @, v-bind: 简写 :
//8. 动态属性:[name]="message"
template:
`<div
@[event]="handleClick"
:[name]="message"
>
{{message}}
</div>`
//9. `<form action="https://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="handleClick" >
// <button type="submit">提交</button>
// </form>
// `
});
const vm= app.mount('#root');数据,方法,计算属性和侦听器
//data: vm.$data.message=123;
//1. computed 和 methods 都能实现的一个功能,建议使用 computed,因为有缓存
//2. computed 和 watcher 都能实现的功能,建议使用 computed 因为更加简洁
const app= Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
message:"hello world",
count:4,
price:5,
newTotal:10,
}
},
watch:{
//price 发生变化时,函数会执行
price(current,prev){
this.newTotal=current*this.count;
}
},
computed:{
//计算属性内部带有缓存机制,作页面渲染的时候会更高效
//当计算属性依赖的内容发生变更时,才会重新执行计算
total(){
return Date.now()+this.count;
// return this.count*this.price;
}
},
methods:{
// formatString(string){
// return string.toUpperCase();
// },
//↓↓ `<div>{{formatString(message)}}</div>`
//只要页面重新渲染,才会重新计算
getTotal(){
return Date.now();
// return this.count*this.price;
}
},
template:
`<div>{{message}}{{total}}</div>`
});
const vm= app.mount('#root');样式绑定语法
<style>
.red{
color: red;
}
.green{
color: green;
}
</style>
<script>
const app= Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
//vm.$data.classString='green'
classString:'red',
classObject:{red:true,green:false},
classArray:['red','green',{brown:false}],
styleString:'color:yellow;background:orange',
styleObject:{
color:'orange',
background:'yellow'
}
}
},
// <demo class="green"/>
template:
`<div :style="styleObject">
hello
</div>`
});
app.component('demo',{
template: `
<div :class="$attrs.class">one</div>
<div >two</div>
`
})
const vm= app.mount('#root');
</script>条件渲染
const app= Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
show:false,
conditionOne:false,
conditionTwo:true,
}
},
//v-show="show" : 频繁改变 dom 的展示与否
template:`
<div v-if="show">hello</div>
<div v-if="conditionOne">if</div>
<div v-else-if="conditionTwo">elseif</div>
<div v-else>else</div>
<div v-show="show">bye</div>
`
});
const vm= app.mount('#root');列表循环渲染
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
listArray: ["dell", "lee", "teacher"],
listObject: {
firstName: "dell",
lastName: "lee",
job: "teacher",
},
};
},
methods: {
handleAddBtnClick() {
//1.使用数组的变更函数 push ,pop ,shift,unshift,splice,sort,reverse
// this.listArray.push('hello');增加新的一个
// this.listArray.pop(); 从下开始删除
// this.listArray.shift();//从开头开始删除
// this.listArray.unshift('hello');//从开头开始新增
// this.listArray.reverse(); //取反
//2.直接替换数组
// this.listArray=['bye','world']
// this.listArray=['bye'].concat(['world'])//bye -- 0 world -- 1
// this.listArray=['bye','world'].filter(item=>item==='bye')//bye -- 0
//3.直接更新数组的内容
// this.listArray[1]='hello'
//直接添加对象的内容,也可以自动的展示出来
// this.listObject.age=100;
// this.listObject.sex='max'
},
},
//循环优先级比 if 高 v-if="key!=='lastName'"不展示 lastname
// 用<template></template>避免外部多一层 div
/*<div>
<div>
teacher -- job
</div>
</div>*/
template: `
<div>
<template
v-for="(value,key,index) in listObject"
:key="index"
>
<div v-if="key!=='lastName'">
{{value}} -- {{key}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<div v-for="item in 10">{{item}}</div>
<button @click="handleAddBtnClick">新增</button>
</div>
`,
});
//dell -- firstName -- 0
//lee -- lastName -- 1
//teacher -- job -- 2
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>事件绑定
- 事件修饰符:@click. stop,prevent(阻止默认行为),capture,self,once
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
counter: 0,
};
},
methods: {
//获取到 event,要额外传递参数,又要获取原生事件对象,使用$evevt
handleBtnClick(num,event) {
this.counter+=1
},
handleDivClick(){
alert('div')
}
},
//1.如果绑定一个事件,执行多个函数的时候,逗号隔开,后面必须加()
//2.@click.stop 当点击 button 时,事件是冒泡的,button 的点击事件会冒泡到上一层的 div 标签上,所以上层的 div 也会感应到点击,停止冒泡就@click.stop
//3.@click.self 点子元素的时候,不要触发自己(div)的 click 事件
//4.@scroll.passive 提升滚动的性能
template: `
<div>
<div @click.self="handleDivClick">
{{counter}}
<button @click.stop="handleBtnClick">button</button>
</div>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");- 按键修饰符 enter, tab, delete, esc, up, down, left, right
const app = Vue.createApp({
methods: {
handleKeyDown(){
console.log('keydown');
}
},
template: `
<div>
<input @keydown.delete= "handleKeyDown"/>
</div>
`
});- 鼠标修饰符: @click. left, right, middle
- 精确修饰符: @click.ctrl.exact
表单中双向绑定指令的使用(1)
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message:''
};
},
methods: {},
// 1.<input v-model="message"/> , 2.textarea 类似
// 3.message:false : <input type="checkbox" v-model="message"/>
//4. message:[] : jack<input type="checkbox" v-model="message" value="jack"/>
template: `
<div>
{{message}}
jack<input type="radio" v-model="message" value="jack"/>
lee<input type="radio" v-model="message" value="lee"/>
</div>`,
});表单中双向绑定指令的使用(2)
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "",
options: [
{
text: "A",
value: {value: "A"},
},
{
text: "B",
value: {value: "B"},
},
{
text: "C",
value: {value: "C"},
},
],
};
},
//单选: <option disabled value=''>请选择内容</option>
template: `
<div>
{{message}}
<select v-model="message" multiple>
<option v-for="item in options" :value="item.value">{{item.text}}</option>
</select>
</div>`,
});表单中双向绑定指令的使用(3)
- 修饰符 lazy,number,trim
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
//问: 如果是 true hello,没有选中 ??
//<input type="checkbox" v-model="message" true-value="hello" false-value="world"/>
message: "123"
};
},
//v-model.lazy 触发 blur 事件的时候,才同步数据的变化:节约触发的时间成本,性能更高
// {{typeof message}}: string <input v-model.number="message" type="number">输入数字之后,string 变成 number
template: `
<div>
{{message}}
<input v-model.trim="message"/>
</div>`,
});探索组件的理念
组件的定义及复用性,局部组件和全局组件
//组件的定义
//组件具备复用性
//全局组件,只要定义了,处处可以使用,性能不高,但是使用起来简单. 名字建议,小写字母单词,中间用横线间隔
//局部组件,定义了,要注册之后才能使用,性能比较高,使用起来有些麻烦. 名字建议,大写字母单词,驼峰命名
//局部组件使用时,要做一个名字和组件间的映射对象,你不写映射,Vue 底层也会自动尝试帮你做映射
//2. 局部组件
// components:{counter},
const Counter={
data(){
return{
count:1
}
},
template:`<div @click="count+=1">{{count}}</div>`
}
// 'hello-world':helloWorld,
const HelloWorld={
template:`<div>hello world</div>`
}
const app = Vue.createApp({
components:{
// counter:Counter,
// 'hello-world':HelloWorld,
Counter,HelloWorld,
},
template:`
<div>
<hello-world/>
<counter/>
</div>`
});
//1. 全局组件
// app.component('counter-parent',{
// template:`<counter/>`
// })
// app.component('counter',{
// data(){
// return{
// count:1
// }
// },
// template:`<div @click="count+=1">{{count}}</div>`
// })
const vm = app.mount('#root');组件间传值及传值校验
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { num:1234}
},
//动态属性传参 :content="num"
template:
`<div><test :content="num"/></div>`
});
//type: String,Boolean[num:true]↑↑↑,Array,Object,Function,Symbol
//required 必填
//default 默认值
app.component('test', {
props: {
content:{
type:Number,
validator:function(value){
return value<1000;
},
default:function(){
return 456;
}
}
},
template: `<div>{{content}}</div>`
})
const vm = app.mount('#root');单项数据流的理解
//2. 属性传的时候,使用 content-abc 这种命名,接的时候,使用 contentAbc 命名
//3. 报错: Attempting to mutate prop "count". Props are readonly.
//单项数据流的概念: 子组件可以使用父组件传递过来的数据,但是绝对不能修改传递过来的数据
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
// content: 1234,
num:1
}
},
//1. v-bind="params" <==> :content="params.content" :a="params.a" :b="params.b" :c="params.c"
template:
// `<div><test :content-abc="content"/></div>`
`<div>
<counter :count="num"/>
</div>`
});
// app.component('test', {
// props: ['contentAbc'],
// template: `<div>{{contentAbc}}</div>`
// })
app.component('counter', {
props: ['count'],
data(){
return{
myCount:this.count,
}
},
//点击,每次修改的是自己组件 data 的内容,是允许修改的
//vue 里面不允许子组件修改父组件的数据,避免组件之间的数据耦合,让代码维护性更好,避免一些潜在的 bug
template: `<div @click="myCount+=1">{{myCount}}</div>`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');Non-Props 属性是什么
//Non-prop 属性
const app = Vue.createApp({
//<counter style="color:red;"/>
template:
`<div>
<counter msg="hello" msg1="hello1"/>
</div>`
});
//`<div msg="hello">Counter</div>`
app.component('counter', {
// inheritAttrs:false, //不添加: msg="hello"
mounted(){
console.log(this.$attrs.msg);
},
template:
//v-bind:msg="$attrs.msg" 加上某个属性
//v-bind="$attrs" 所有父组件传递的 Non-prop 属性,都会加到这第二个 div
`<div v-bind:msg="$attrs.msg">Counter</div>
<div v-bind="$attrs">Counter</div>`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');父子组件间如何通过事件进行通信
//父子组件如果存在双向绑定关系的时候,可以把复杂的代码缩减
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return { count : 1}
},
methods:{
handleAdd(count){
this.count+=count;
}
},
//监听事件用-,触发事件用驼峰
//modelValue =>count
//:modelValue="count" @add="handleAdd" => v-model="count"
//v-model:app="count"
template:
`<counter v-model="count"/>`
});
app.component('counter', {
props:['modelValue'],//app
// emits:{
// add:(count)=>{
// if(count>0){
// return true;
// }
// return false;
// }
// },
//update:modelValue [固定的] => add
methods:{
handleClick(){
//app => modelValue
this.$emit('update:modelValue',this.modelValue+3);
}
},
template:
`<div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');组件间双向绑定高级内容(选学)
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
count: 'a',
}
},
template:
`<counter v-model.uppercase="count"/>`
});
app.component('counter', {
props: {
//modelModifiers 传递过来的修饰符
'modelValue': String,
'modelModifiers': {
default: () => ({})
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
let newValue=this.modelValue+'b';
if(this.modelModifiers.uppercase){
newValue=newValue.toUpperCase();
}
this.$emit('update:modelValue', newValue);
}
},
template:
`<div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div>`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');使用插槽和具名插槽解决组件内容传递问题(1)
const app = Vue.createApp({
//slot 中使用的数据,作用域的问题
//父(子)模板里调用的数据属性,使用的都是父(子)模板里的数据
data(){
return { text :'提交'}
},
// <div>提交</div> 插槽 slot
template:
`
<myform>
<div>{{text}}</div>
</myform>
<myform>
<button>{{text}}</button>
</myform>
<myform>
</myform>
`
});
app.component('myform', {
methods: {
handleClick(){
alert(123)
}
},
template:
// <slot>default volue</slot> 无插槽时,有默认值
`<div>
<input/>
<span @click="handleClick">
<slot>default volue</slot>
</span>
</div>`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');(2)
//具名插槽
const app = Vue.createApp({
template:`
<layout>
<template v-slot:header>
<div>header</div>
</template>
<template v-slot:footer>
<div>footer</div>
</template>
</layout>
`
});
app.component('layout', {
template:
`<div>
<slot name="header"></slot>
<div>content</div>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</div>`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');作用域插槽
//当子组件的内容要由父组件决定的时候,用这个作用域插槽实现
const app = Vue.createApp({
//简写 #header -> v-slot:header
//对象解构
template: `
<list v-slot="{item}">
<div>{{item}}</div>
</list >
`
});
app.component('list', {
data() { return { list: [1, 2, 3] } },
template:
`<div>
<slot v-for="item in list" :item="item"/>
</div>`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');动态组件和异步组件
- 动态组件
//动态组件: 根据数据的变化,结合 component 这个标签,来随时动态切换组件的显示
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return {currentItem:'input-item'}
},
methods:{
handleClick(){
if(this.currentItem==='input-item'){
this.currentItem='common-item';
}else{
this.currentItem='input-item';
}
}
},
//keep-alive> 保存原先输入内容
template: `
<keep-alive>
<component :is="currentItem"/>
</keep-alive>
<button @click="handleClick">切换</button>
`
});
app.component('input-item', {
template: `<input />`
});
app.component('common-item', {
template: `<div>hello world</div>`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');- 异步组件,,同步组件用的多
//异步组件:
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>
<common-item/>
<async-common-item/>
</div>
`
});
app.component('common-item', {
template: `<div>hello world</div>`
});
app.component('async-common-item',Vue.defineAsyncComponent(()=>{
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve({
template:`<div>this is an async component</div>`
})
},4000)
})
}))
const vm = app.mount('#root');基础语法知识点查缺补漏
//1. v-once 让某个元素标签只渲染一次
// ref 获取 Dom 节点 / 组件引用 的一个语法
// provide / inject 多值传递
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return {count:1}
},
provide(){
return{
count:this.count,
}
},
// mounted(){
// console.log(this.$refs.common.sayHello());
// },
// <common-item ref="common"/>
//// <div @click="count+=1" v-once> 只渲染一次,1 一直
template: `
<div>
<child :count="count"/>
<button @click="count+=1">Add</button>
</div>
`
});
app.component('child', {
// methods:{
// sayHello(){
// alert('hello world')
// }
// },
template: `<child-child :count="count"/>`
});
app.component('child-child', {
inject:['count'],
template: `<div>{{count}}</div>`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');Vue 中的动画
使用 Vue 实现基础的 CSS 过渡与动画效果
<style>
/* 动画
@keyframes leftToRight{
0%{
transform: translateX(-100px);
}
50%{
transform: translateX(-50px);
}
0%{
transform: translateX(0px);
}
}
.animation{
animation: leftToRight 3s;
} */
.transition{
transition: 3s background-color ease;
}
/* .blue{
background: blue;
}
.green{
background: green;
} */
</style>
<script>
//过渡,动画
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return {
styleObj:{
background:'blue'
}
// animate:{
// // animation:false
// transition:true,
// blue:true,
// green:false
// }
}
},
methods:{
handleClick(){
// this.animate.blue=!this.animate.blue
// this.animate.green=!this.animate.green
if(this.styleObj.background==='blue'){
this.styleObj.background='green';
}else{
this.styleObj.background='blue';
}
}
},
template: `
<div>
<div class="transition" :style="styleObj">hello world</div>
<button @click="handleClick">切换</button>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');使用 transition 标签实现单元素组件的过渡和动画效果
- (1) 封装
<style>
@keyframes shake{
0%{
transform: translateX(-100px);
}
50%{
transform: translateX(-50px);
}
100%{
transform: translateX(50px);
}
}
.v-leave-active{
animation:shake 3s;
}
.v-enter-active{
animation:shake 3s;
}
</style>
<script>
//单元素/单组件的入场出场动画
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
show: false,
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.show = !this.show;
}
},
//<transition name="hello"> hello -> v 上 style
template: `
<div>
<transition>
<div v-if="show">hello world</div>
</transition>
<button @click="handleClick">切换</button>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');- (2)
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
show: false,
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.show = !this.show;
},
handleBeforeEnter(el){
el.style.color="red";
},
handleEnterActive(el,done){
const animation= setInterval(()=>{
const color=el.style.color;
if(color==='red'){
el.style.color="green";
}else{
el.style.color="red";
}
},1000)
setTimeout(()=>{
clearInterval(animation);
done();
},3000);
// setTimeout()
},
handleEnterEnd(){
alert(123);
}
},
//<transition type="animation"> 控制动画和过渡同步执行的效果
//:duration="{enter:1000,leave:3000}" 控制时间
template:
//el, el done,el,el,el done,el
`
<div>
<transition
:css="false"
@before-enter="handleBeforeEnter"
@enter="handleEnterActive"
@after-enter="handleEnterEnd"
@before-leave=
@leave=
@leave-after=
>
<div v-show="show">hello world</div>
</transition>
<button @click="handleClick">切换</button>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');组件和元素切换动画的实现
<style>
.v-leave-to{
opacity: 0;
}
.v-enter-from{
opacity: 0;
}
.v-enter-active,
.v-leave-active{
transition: opacity 1s ease-in;
}
.v-enter-to,
.v-leave-from{
opacity: 1;
}
</style>
<script>
//多个单元素标签之间的切换
//多个单组件之间的切换
const ComponentA={
template:'<div>hello world</div>'
}
const ComponentB={
template:'<div>bye world</div>'
}
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
// show: false
component:'component-a'
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
// this.show = !this.show;
if(this.component === 'component-a'){
this.component='component-b';
}else{
this.component='component-a';
}
},
},
components:{
'component-a':ComponentA,
'component-b':ComponentB,
},
template:
//in-out : 先进来,再慢慢隐藏
//appear : 第一次进来,,也会有渐变
//单组件写法 <div v-else="show">bye world</div>
`
<div>
<transition mode="out-in" appear>
<component :is="component"/>
</transition>
<button @click="handleClick">切换</button>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');列表动画
- 作业: 移除动画,点击数字可以删除的功能
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/animate.css/4.1.1/animate.min.css"
/>
<style>
/* 入场 */
.v-enter-from {
opacity: 0;
transform: translateY(30px);
}
.v-enter-active {
transition: all 0.5s ease-in;
}
.v-enter-to {
opacity: 1;
transform: translateY(0);
}
.v-move {
transition: all 0.5s ease-in;
}
.list-item {
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 10px;
}
</style>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
//列表动画的实现
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
list: [1, 2, 3],
};
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.list.unshift(this.list.length + 1);
},
},
template: `
<div>
<transition-group>
<span class="list-item" v-for="item in list" :key="item">{{item}}</span>
</transition-group>
<button @click="handleClick">增加</button>
</div>
`,
});
const vm=app.mount('#root')
</script>
</html>状态动画
//状态动画,svg
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
number: 1,
animateNumber: 1
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.number = 10;
if (this.animateNumber < this.number) {
const animation = setInterval(() => {
this.animateNumber += 1;
if (this.animateNumber === 10) {
clearInterval(animation);
}
}, 100);
}
},
},
template:
`
<div>
<div>{{animateNumber}}</div>
<button @click="handleClick">增加</button>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');Vue 中的高级语法
Mixin 混入的基础语法(1)
//组件 data,methods 优先级高于 mixin data,methods 的优先级,
//生命周期函数,mixin 的先执行,后执行组件里面的
const myMixin = {
data() {
return { number: 2,count:1 };
},
created(){
console.log('mixin created');
},
methods:{
handleClick() {
console.log("mixin handleClick");
},
}
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {number:1};
},
created(){
console.log('created');
},
mixins: [myMixin],
methods: {
handleClick() {
console.log("handleClick");
},
},
template: `
<div>
<div>{{number}}</div>
<child/>
<button @click="handleClick">增加</button>
</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");Mixin 混入的基础语法(2)
//全局 mixin 维护性不高
const myMixin = {
number: 1,
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
mixins:[myMixin],
//自定义属性,组件中的属性优先级高于 mixin 属性的优先级
number: 2,
template: `
<div>
<div>{{this.$options.number}}</div>
</div>
`,
});
//修改优先级
app.config.optionMergeStrategies.number=(mixinVal,appValue)=>{
return mixinVal||appValue
}开发实现 Vue 中的自定义指令(1)
/*局部指令
const directives = {
focus: {
mounted(el) {
el.focus();
},
},
};*/
//自定义指令 directive
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
hello:true
}
},
//局部: directives:directives,
template: `
<div>
<div v-if="hello">
<input v-focus/>
</div>
</div>
`,
});
app.directive("focus", {
beforeMount(el) {
console.log("beforeMount");
},
mounted(el) {
console.log("mounted");
el.focus();
},
beforeUpdate(){
console.log("beforeUpdate");
},
updated(){
console.log('updated');
},
//即将销毁
beforeUnmount(){
console.log('beforeUnmount');
},
//销毁过后
unmounted(){
console.log('unmounted');
}
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");开发实现 Vue 中的自定义指令(2)
.header{
position: absolute;
} const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
distance:110
}
},
//v-pos:left="distance" 距离左侧有距离
template: `
<div>
<div v-pos:left="distance" class='header'>
<input/>
</div>
</div>
`,
});
//简写 ↓ mounted,undated : top:300 <div v-pos="top" class='header'>
app.directive('pos',(el,binding)=>{
el.style[binding.arg]=(binding.value+'px')
})
// app.directive("pos", {
// mounted(el,binding){
// el.style.top=(binding.value+'px')
// },
// //当数据发生变化时,组件要重新渲染,这会重新重置一下高度
// undated(el,binding){
// el.style.top=(binding.value+'px')
// }
// });
const vm = app.mount("#root");Teleport 传送门功能
<style>
.area {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
background: green;
}
.mask {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: #000;
opacity: 0.5;
color: #fff;
font-size: 100px;
}
</style>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<div id="hello"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
show: false,
message:'hello'
};
},
methods: {
handleBtnClick() {
this.show = !this.show;
},
},
//<teleport to="body"> 传递给 body,蒙层铺满屏幕
//在蒙层显示文字
template: `
<div class="area">
<button @click="handleBtnClick">按钮</button>
<teleport to="body">
<div class="mask" v-show="show">{{message}}</div>
</teleport>
</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>更加底层的 render 函数(选学)
//render function
//template -> render -> h -> 虚拟 DOM(JS 对象)->真实 DOM ->展示到页面上
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<my-title :level="2">
hello de
</my-title>
`,
});
//展示不同大小的标题 hello
app.component("my-title", {
props:['level'],
render(){
const {h}=Vue;
//虚拟 dom: 1.可以让 vue 的性能更快 2.让 vue 具备一个跨平台的能力 (weex 开发工具去编写移动端的代码)
/*
{
tagName:'div',
attributes:{},
text:'hello',
}
*/
return h("h" + this.level, {}, [
this.$slots.default(),
//无限嵌套
h("h4", {}, "dell"),
]); //返回虚拟 dom 节点的函数
}
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");插件的定义和使用
//plugin 插件,也是把通用性的功能封装起来
const myPlugin = {
install(app, options) {
app.provide("name", "delllee");
app.directive("focus", {
mouted(el) {
el.focus();
},
});
app.mixin({
mounted() {
console.log("mixin");
},
});
app.config.globalProperties.$sayHello = "hello world";
},
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<my-title />
`,
});
app.component("my-title", {
inject: ["name"],
mounted() {
console.log(this.$sayHello);
},
template: `<div>{{name}}<input v-focus/></div>`,
});
app.use(myPlugin, { name: "dell" });
const vm = app.mount("#root");数据校验插件开发实例
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
name: "dell",
age: 28,
};
},
rules: {
age: {
validate: (age) => age > 25,
message: "too young",
},
name: {
validate: (name) => name.length >= 4,
message: "name too short",
},
},
template: `
<div>name:{{name}},age:{{age}}</div>
`,
});
const validatorPlugin = (app, options) => {
app.mixin({
created() {
for (let key in this.$options.rules) {
const item = this.$options.rules[key];
this.$watch(key, (value) => {
const result = item.validate(value);
if (!result) console.log(item.message);
});
}
},
});
};
app.use(validatorPlugin)
const vm = app.mount("#root");Composition API
Setup 函数的使用
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{name}}</div>
`,
methods: {
test() {
console.log(this.$options.setup());
},
},
mounted() {
this.test();
},
//created 实例被完全初始化之前
setup(props, context) {
return {
name: "dell",
handleClick: () => {
alert(123);
},
};
},
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");ref,reactive 响应式引用的用法和原理(1)
//ref, reactive 响应式的引用
//原理: 通过 proxy 对数据进行封装, 当数据变化时, 触发模板等内容的更新
//ref 处理基础类型的数据
//reactive 处理非基础类型的数据
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>{{nameObj[0]}}</div>
`,
setup(props, context) {
/*(1)
const {ref}=Vue;
proxy,'dell'变成 proxy({value:'dell'})这样的一个响应式引用
let name = ref('dell');
setTimeout(() => {
name.value = "lee";
}, 2000);
return { name };*/
const { reactive } = Vue;
//proxy,{ name: "dell" }变成 proxy({ name: "dell" })这样的一个响应式引用
const nameObj = reactive([123]);
setTimeout(() => {
nameObj[0] = 456;
}, 2000);
return { nameObj };
},
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");ref,reactive 响应式引用的用法和原理(2)
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>{{name}}</div>
`,
setup(props, context) {
const { reactive,readonly,toRefs } = Vue;
const nameObj = reactive({name:'dell',age:28});
//copy 出来的不能被响应式修改的
//const copyNameObj=readonly(nameObj)
setTimeout(() => {
nameObj.name='lee'
// nameObj[0] = 456;
// copyNameObj[0]=456
}, 2000);
/*toRefs
proxy({name:'dell',age:28}),{
name:proxy({value:'dell'}),
age:proxy({value:28})
}
*/
const {name}=toRefs(nameObj);
return { name };
},
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");toRef 以及 context 参数(1)
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>{{age}}</div>
`,
setup(props, context) {
//toRefs 从 data 这响应式对象时找数据的时候,
//如果找不到的话,不会给 age 默认的响应式引用,而是给 undefined
const { reactive,toRef } = Vue;
const data = reactive({name:'dell'});//但是最好给个默认值 age:0
const age=toRef(data,'age')//取不到数据则置空
setTimeout(()=>{
age.value='lee'
},2000)
return { age };
},
});toRef 以及 context 参数(2)
const app = Vue.createApp({
methods: {
handleChange() {
alert("change");
},
},
template: `<child @change='handleChange'>parent</child>`,
});
//父组件传递给子组件
app.component("child", {
mounted() {
// console.log(this.$slots);
this.$emit("change");
},
template: '<div @click="handleClick">123324</div>',
setup(props, context) {
const { h } = Vue;
//通过 slots 可以实现传统的 this.$slots 的作用,
//emit 可以实现传统语法中的 this.$emit 的向上触发的一个功能
const { attrs, slots, emit } = context;
// console.log(attrs);//获取 None-Props 属性的内容
// return ()=>h('div',{},slots.default())
function handleClick() {
emit("change");
}
return {
handleClick,
};
},
});使用 Composition API 开发 TodoList
//关于 list 操作的内容进行了封装
const listRelativeEffect = () => {
const { reactive } = Vue;
const list = reactive([]);
const addItemToList = (item) => {
list.push(item);
};
return { list, addItemToList };
};
//关于 inputValue 操作的内容进行了封装
const inputRelativeEffect = () => {
const { ref } = Vue;
const inputValue = ref("");
const handleInputValueChange = (e) => {
inputValue.value = e.target.value;
};
return { inputValue, handleInputValueChange };
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
//流程调度中转
const { list, addItemToList } = listRelativeEffect();
const { inputValue, handleInputValueChange } = inputRelativeEffect();
return {
list,
addItemToList,
inputValue,
handleInputValueChange,
};
},
template: `
<div>
<div>
<input :value="inputValue" @input="handleInputValueChange"/>
<button @click="()=>addItemToList(inputValue)">提交</button>
</div>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in list" :key="index">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
`,
});computed 方法生成计算属性
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const { ref, reactive,computed } = Vue;
const countObj=reactive({count:0})
// const count = ref(0);
const handleClick = () => {
// count.value += 1;
countObj.count+=1
};
let countAddFive = computed({
get: () => {
// return count.value + 5;
return countObj.count + 5;
},
set: (param) => {
// count.value = param-5;//95--100
countObj.count=param-5;
},
});
setTimeout(() => {
countAddFive.value = 100;
}, 3000);
return { countObj, handleClick, countAddFive };
},
template: `
<div>
<span @click="handleClick">{{countObj.count}}</span>--{{countAddFive}}
</div>
`,
});watch 和 watchEffect 的使用和差异性(1)
//watch 侦听器
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const { ref, reactive, watch, toRefs } = Vue;
const nameObj = reactive({ name: "dell" ,enName:'lee'});
// 具备一定的惰性 lazy
// 参数可以拿到原始和当前值
// const name = ref("dell");
// watch(name, (currentValue, prevValue) => {
// console.log(currentValue, prevValue);
// });
watch(
[() => nameObj.name,() => nameObj.enName],
([curName,curEng],[prevName,preEng]) => {
console.log(curName,curEng,'---',prevName,preEng);
}
);
const { name ,enName} = toRefs(nameObj);
return { name,enName };
},
template: `
<div>
<div>
Name: <input v-model="name"/>
</div>
<div>
Name is {{name}}
</div>
<div>
Name: <input v-model="enName"/>
</div>
<div>
Name is {{enName}}
</div>
</div>
`,
});watch 和 watchEffect 的使用和差异性(2)
- watch 侦听器
- watchEffect 侦听器,偏向于 effect
watch(
[() => nameObj.name,() => nameObj.enName],
([curName,curEng],[prevName,preEng]) => {
console.log('watch',curName,prevName,'---',curEng,preEng);
},{immediate:true}
);
//立即执行,没有惰性 immediate
const stop = watchEffect(() => {
//有些异步操作
//有依赖,改变时都会重新执行,输出改的值,
//不需要传递你要侦听的内容,自动会感知代码依赖,不需要传递很多参数,只要传递一个回调函数
//watchEffect 不能获取之前数据的值
console.log(nameObj.name);
setTimeout(() => {
stop();
}, 5000);
});生命周期函数的新写法
const { ref, onBeforeMount, onMounted, onBeforeUpdate, onUpdated ,onRenderTracked,onRenderTriggered} =
Vue;
const name = ref("dell");
onBeforeUpdate(() => {
console.log("onBeforeUpdate");
});
//在页面重新渲染的时候,每次渲染之后,vue 都会重新收集响应式的依赖,就会执行
onRenderTracked(()=>{
console.log('onRenderTracked');
})
//重新触发页面渲染才会执行
onRenderTriggered(()=>{
console.log('onRenderTriggered');
})
const handeClick = () => {
name.value = "lee";
};
return { name, handeClick };
},
template: `
<div @click="handeClick">
{{name}}
</div>
`,
});Provide,Inject,模版 Ref 的用法
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const {provide,ref,readonly}=Vue;
const name=ref('dell');
provide('name',readonly(name))
provide('changeName',(value)=>{
name.value=value
})
return {};
},
template: `
<div>
<child/>
</div>
`,
});
app.component('child',{
setup(){
const {inject}=Vue;
const name=inject('name')
const changeName=inject('changeName')
//在子组件修改父组件的数据,不符合单向数据流的要求
const handleClick=()=>{
// name.value='lee'// ×
changeName('lee')
}
return {name,handleClick}
},
template:'<div @click="handleClick">{{name}}</div>'
})- dom ref
- CompositionAPI 的语法下,获取真实的 DOM 元素节点
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const {ref,onMounted}=Vue
const hello=ref(null)
onMounted(()=>{
console.log(hello.value);
})
return {hello};
},
template: `
<div>
<div ref="hello">hello w</div>
</div>
`,
});使用单文件组件编写 TodoList
<template>
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue"/>
<button class="button" @click="handleAddItem">提交</button>
</div>
<ul>
<list-item v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="index" :msg="item"/>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, ref } from "vue";
import ListItem from './components/ListItem'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{
ListItem
},
setup() {
const inputValue=ref('')
const list = reactive([]);
const handleAddItem=()=>{
list.push(inputValue.value)
inputValue.value=''
}
return {inputValue, list ,handleAddItem};
},
};
</script>Vue-Router 路由的理解和使用
- router-link 是跳转路由的标签
- router-view 负责展示当前路由对应的组件内容
- 异步加载路由 : 访问该页面的时候,才去加载该页面
component: () => import(/ webpackChunkName: "about" / '../views/AboutView.vue')
VueX 的语法详解(1)
- src/store/index.js
//VueX 数据管理框架
//VueX 创建了一个全局唯一的仓库,用来存放全局的数据
export default createStore({
state: {
name:'dell'
},
})<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>{{myName}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "HomeView",
computed: {
myName() {
return this.$store.state.name;
}
}
};
</script>VueX 的语法详解(2)
<template>
<div class="about">
<h1 @click="handleClick">This is an about page</h1>
<h1>{{ myName }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "AboutView",
computed: {
myName() {
return this.$store.state.name;
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
//想改变数据,vuex 要求第一步,必须派发一个 action
//如果不涉及到异步操作,只是同步修改数据,可以简化代码,直接提交 数据的修改
// this.$store.commit('change') 将 store/index.js 中的 actions 注释
/**
* 1.dispatch 方法,派发一个 action,名字叫做 change
* 2.感知到 change 这个 action,执行 store 中 actions 下面的 change 方法
* 3.commit 提交一个叫做 change 的数据改变
* 4.mutation 感知到提交的 change 改变,执行 change 方法改变数据
*/
this.$store.dispatch('change','hello');
}
}
};
</script>- src/store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
//VueX 数据管理框架
//VueX 创建了一个全局唯一的仓库,用来存放全局的数据
export default createStore({
state: {
name:'dell'
},
getters: {
},
//mutation 里面只允许写同步代码,不允许写异步代码,
//commit 和 mutation 做关联
mutations: {
//第四步,对应的 mutation 被执行
change(state,str){
//第五部,在 mutation 里面修改数据
//在 action 中写异步操作: setTimeout(()=>{
state.name='lee'
//},2000)
}
},
//放异步代码
//dispatch 和 actions 作关联
actions: {
//第二步,store 感知到你出发了一个叫做 change 的 action,执行 change 方法
change(store,str){
//第三步,提交一个 commit,触发一个 mutation
setTimeout(()=>{
store.commit('change',str)
},2000)
}
},
modules: {
}
})CompositionAPI 中如何使用 VueX
<template>
<div class="about">
<h1 @click="handleClick">This is an about page</h1>
<h1>{{ name }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//解构
import {toRefs} from "vue";
import {useStore} from "vuex";
export default {
name: "AboutView",
setup() {
const store = useStore();
const {name} = toRefs(store.state);
const handleClick = () => {
// store.commit('changeName','hello')
store.dispatch("getData");
};
return {name, handleClick};
}
};
</script>- src/store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
name:'dell'
},
mutations: {
changeName(state,str){
state.name=str
}
},
actions: {
getData(store){
setTimeout(()=>{
store.commit('changeName','hello2')
},2000)
}
}
})使用 axios 发送 ajax 请求
- npm install axios -S
<template>
<div class="about">
<h1 @click="handleClick">This is an about page</h1>
<h1>{{ name }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//解构
import {toRefs} from "vue";
import {useStore} from "vuex";
export default {
name: "AboutView",
setup() {
const store = useStore();
const {name} = toRefs(store.state);
const handleClick = () => {
// store.commit('changeName','hello')
store.dispatch("getData");
};
return {name, handleClick};
}
};
</script>import { createStore } from 'vuex'
import axios from "axios";
export default createStore({
state: {
name:'dell'
},
mutations: {
changeName(state,str){
state.name=str
}
},
actions: {
getData(store){
axios.get('https://www.fastmock.site/mock/ae8e9031947a302fed5f92425995aa19/jd/api/user/register')
.then((response)=>{
const msg=response.data.desc
store.commit('changeName',msg)
})
}
}
})